共軛高分子PTD體外造影劑輔助近紅外二區光聲顯微成像
體外造影劑輔助的近紅外二區光聲顯微成像技術可以解析三維廣面積/大深度,高信號/背景比例,高成像深度/深度分辨率比例的生物組織。
具有強近紅外二區吸光系數的共軛高分子納米顆粒輔助的三維高分辨率光聲顯微成像,實現了腦部和部位的心血管的微米分辨率,毫米穿透深度,高信號/背景比例的原位活體成像。此文成像效果比近紅外二區熒光三維激光共聚焦成像效果更有優勢。
背景介紹
生物組織三維成像技術可以用來解析血管和結構,有利于分析生理/病理過程,是目前成像技術發展的前沿。傳統三維成像技術各自有一定局限性。比如核磁, PET 和 CT 成像分辨率不足。雙光子和近紅外二區熒光激光共聚焦成像的視野狹小,其成像質量有待進一步提高。光聲顯微成像能夠調節分辨率和成像深度,是近年來新興的成像技術。相對于近紅外一區/可見光光聲顯微成像,近紅外二區光聲顯微成像能夠就降低光散射/生物組織光吸收對成像的干擾。此前報道的近紅外二區光聲成像大都使用體內造影劑來成像, 但是生物組織容易產生強噪音干擾,使體內造影劑輔助近紅外二區光聲成像表現出低信號/背景比例,模糊的成像效果。
研究出發點
體外造影劑能夠**提高成像質量. 適用于活體成像的造影劑需要生物相容性好,光穩定性好,吸光系數大,弱熒光,可大規模制備等特點. 有機共軛高分子可以滿足這些條件. 于是, 我們設計了一個新型, 微流控技術制備的具有強近紅外二區吸收的共軛高分子納米顆粒, 來輔助實現三維近紅外二區顯微光聲成像。
圖文解析
劉斌課題組設計了新型電子給體-電子受體1 -電子給體-電子受體2 結構構成的共軛高分子 PTD, 使用課題組自制的微流控技術制備了大小可控且尺寸均一的納米顆粒(40 納米左右). 該納米顆粒在吸收峰 1161 納米左右的吸光系數 高達 48.1 L g-1, 有利于實現光聲造影 (如圖1 所示)。
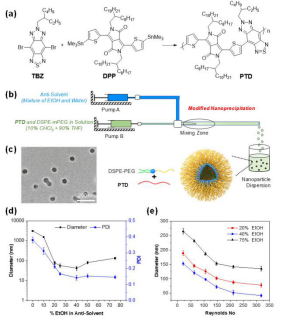
▲Figure 1. (a) The synthetic route towards PTD. Reagents and conditions: Pd2(dba)3, P(o-tyl)3, anhydrous toluene, 100 oC, 48 h; (b) Schematic diagram of microfluidic glass capillary mixer for the synthesis of monodisperse PTD NPs through modified nanoprecipitation. (c) TEM image of PTD NPs synthesized at Re 320 with 40% EtOH in the anti-solvent. (d) Changes in the size and PDI of PTD NPs by varying the amount of EtOH in the antisolvent from 0 to 75% at Re 320. (e) Variation in the size of PTD NPs with 25, 40 and 75% EtOH in the anti-solvent at different Re.
同時, 如圖2 所示, 我們使用該納米顆粒實現了耳朵上皮下肝的血管三維成像. 先, 在未注釋納米顆粒前,調整光聲成像參數,使背景信號降低到較低. 注射納米顆粒后,使用 1064 納米脈沖激光, 實現了部位的無損廣面積成像. 成像面積高達 7 毫米× 7 毫米, 成像深度達 0.76 毫米. 在 755 微米成像深度處, 分辨率是 25.9 微米, 信號/背景比例是 26.0 dB, 成像深度/深度分辨率高達 29.1 倍. 同時通過定性和定量比對部位和周圍正常組織的血管密度, 邊界可以勾畫出來. 本研究的近紅外二區光聲顯微成像效果比較近報道的近紅外二區熒光三維共聚焦成像效果好.可能原因有三個: (1) 本實驗使用的 1064 納米激發光比近紅外二區熒光成像使用的808納米激光的光散射效應更低; (2) 光聲成像的聲波散射比熒光成像的光散射效應更低; (3) PTD 納米顆粒吸光系數大, 可以較大限度的背景噪音. 然而二區熒光中的活體自發熒光比較強, 產生的噪音干擾不可忽略。
此外, 如圖3 所示, 我們使用 PTD 納米顆粒實現了透過老鼠頭骨腦血管的三維高分辨(分辨率 25.4 微米),高信號/背景比例( 22.3 dB)成像. 其成像深度高達 1001 微米. 該腦血管光聲成像效果比較近報道的雙光子成像和近紅外二區熒光共聚焦成像的效果好.
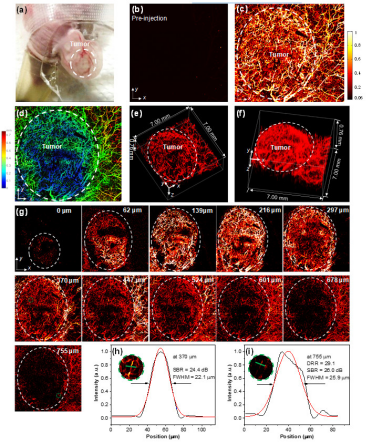
▲Figure 2. PA imaging of subcutaneous HepG2 tumor-bearing mouse ear with a colorbar 0.06-1. (a) Photo of mouse ear bearing subcutaneous tumor for PA imaging. Representative xy projected tumor bearing mouse ear image (7.00 × 7.00 mm, x × y) before (b) and after (c) PTD NP administration. (d) Depth-encoded maximum amplitude projection image corresponding to Figure c (The PA signal color changes correspond to different depths according to the color chart for depth information on the right side). (e) and (f) 3D reconstruction of tumor-bearing mouse ear vasculature images from different view side (7.00 × 7.00 × 0.76 mm, x × y × z) and the tumor margin was labelled with white-dashed circle. (g) Layer-by-layer PA images (7.00 × 7.00 mm, x × y) of subcutaneous tumor-bearing mouse ear with white-dashed circle for labelling tumor margin in each layer. (h) and (i) The PA intensity profile (black curve) along the green line in the zoomed area (insets, Figures h and i) which represents the area labelled with green-dashed circle at depths of 370 and 755 μm, respectively. The Gaussian fits to the profiles are presented using red curves. Gaussian-fitted full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the vessel along the green line is presented at different depth.
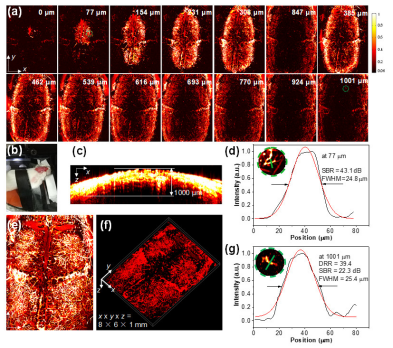
▲Figure 3. In vivo ORPAMI of whole-cortex brain through intact skull after administration of PTD NPs through tail-vain (colorbar: 0.06-1). (a) Layer-by-layer PA images (8 × 6 mm, x × y) of mouse brain. The deepest area reached 1001 μm. (b) Photo of mouse for imaging. (c) Representative xz projected brain vasculature image (8 × 1 mm, x × z). (e) Representative xy projected brain vasculature image (8 × 6 mm, x × y). (f) 3D reconstruction of brain vasculature (8 × 6 × 1 mm, x × y × z). (d) and (g) The PA intensity profiles along the green line in the zoomed area (inset, Figure d and g) which represents the area labelled with green-dashed circle (Figure a) at the depths of 77 and 1001 μm, respectively. The Gaussian fits to the profile are shown in red curve. Gaussian-fitted full width at half maximum (FWHM) of the vessel along the green line is presented at different depth.
總結與展望
實現了體外造影劑輔助近紅外二區光聲顯微成像. 微流控技術制備共軛高分子, 可以實現尺寸可控, 形貌均一. 同時,共軛高分子生物相容性好,吸光系數大,光聲穩定性好,是很好的活體成像的光聲造影劑. 我們證明二區共軛高分子輔助光聲顯微成像可以準確勾畫邊界, 解析內部和周圍正常組織血管結構, 準確成像腦補三維復雜血管脈絡. 因此, 共軛高分子納米顆粒是很有潛力的活體成像造影劑, 用來理解生理和病理過程。
wyf 04.01




 齊岳微信公眾號
齊岳微信公眾號 官方微信
官方微信 庫存查詢
庫存查詢